EPCQ16ASI8N Configuration PROMs: Features, Applications and Datasheet
2025-03-11 09:10:08 1515
EPCQ16ASI8N Description
The Intel EPCQ16ASI8N is a serial configuration flash memory device primarily used for storing FPGA configuration bitstreams. Manufactured with advanced flash technology, it offers non-volatile storage with high data retention and fast read access. Its design emphasizes reliability and low power consumption, making it ideal for use in high-performance programmable logic devices. The device is available in a compact, lead-free package suitable for space‐constrained applications.
EPCQ16ASI8N Features
16 Megabit Capacity: Provides ample space for storing configuration bitstreams for mid-range FPGA devices.
High-Speed Serial Interface: Optimized for fast programming and quick read access, supporting serial clock frequencies up to around 50 MHz.
Low Power Consumption: Designed for energy efficiency with minimal standby power, ideal for battery-operated systems.
Robust Data Retention: Engineered with advanced error-checking and protection circuitry to ensure reliable operation even after repeated power cycles.
Compact, Lead-Free Packaging: Offered in a small, environmentally friendly package that minimizes board space usage while meeting industry standards.
EPCQ16ASI8N Applications
FPGA Configuration Storage: Used to store and deliver configuration bitstreams for FPGAs in a variety of electronic systems.
Embedded Systems: Ideal for systems requiring reliable non-volatile memory for startup configuration, such as industrial controllers and automotive electronics.
Consumer Electronics: Integrated into devices where a compact, low-power configuration memory is essential.
High-Reliability Applications: Suitable for environments that demand robust performance over wide temperature ranges and under harsh conditions.
Prototyping and Mass Production: Frequently used in both development and final product deployments to ensure consistent FPGA behavior.
EPCQ16ASI8N CAD Model
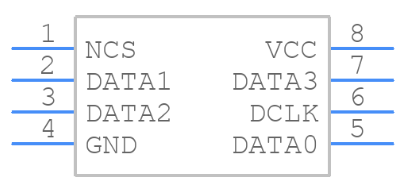
Symbol
Footprint
3D Model
EPCQ16ASI8N Alternatives
EPCQ8 Series: A lower capacity version suitable for simpler FPGA configurations.
EPCQ32 Series: Offers higher capacity for larger designs.
Other Serial Flash Devices (e.g., Micron’s MT25Q Series): Similar devices that offer comparable performance and reliability.
Intel’s Other Configuration Memories: Such as variants in the EPCQ family tailored for different FPGA families.
Third-Party Alternatives: Providers like Cypress and Macronix also offer serial flash memories with similar specifications.
EPCQ16ASI8N Manufacturer
Intel Corporation is a global leader in semiconductor innovation, renowned for pioneering microprocessor technology and powering modern computing systems. Founded in 1968, Intel has continually pushed the boundaries of performance and efficiency in processors, memory, and integrated solutions, serving markets from personal computers and data centers to artificial intelligence and autonomous systems. With a strong focus on research and development, Intel drives advancements in high-performance computing, connectivity, and power-efficient designs, making it a key player in the digital transformation across industries worldwide.
EPCQ16ASI8N FAQs
How does the EPCQ16ASI8N ensure reliable configuration during rapid power cycling?
The device incorporates built-in error-checking and a redundant sector architecture, allowing it to verify the integrity of the stored bitstream during power-up and quickly recover from intermittent power issues.
What is the maximum serial clock frequency the EPCQ16ASI8N supports, and how does it maintain signal integrity?
The EPCQ16ASI8N supports serial clock frequencies up to approximately 50 MHz. It employs internal calibration and robust ESD protection on its serial lines to maintain high signal integrity even at high speeds.
What measures are built into the EPCQ16ASI8N to protect against transient voltage spikes and environmental stresses?
The device features integrated ESD protection and surge tolerance circuitry, along with an error-correcting code (ECC) mechanism, ensuring that configuration data is not corrupted by voltage transients or environmental interference.
What PCB layout best practices are recommended for using the EPCQ16ASI8N to minimize signal degradation?
Designers should use controlled impedance traces, minimize trace lengths between the flash memory and the FPGA, deploy adequate decoupling capacitors near the device, and consider proper termination resistors to reduce ringing and crosstalk.
Does the EPCQ16ASI8N support dual-configuration images for enhanced reliability, and how can this feature be utilized?
Yes, the EPCQ16ASI8N is capable of supporting dual configuration images, allowing a secondary, backup configuration to be stored and automatically loaded if the primary configuration fails, thereby enhancing system reliability in mission-critical applications.




