EPCS4SI8N FPGA: Features, Alternatives and Applications
2024-10-09 11:32:51 952
EPCS4SI8N Description
The EPCS4SI8N is a serial configuration memory device manufactured by Intel (formerly Altera) used to store configuration data for FPGAs (Field-Programmable Gate Arrays). This particular memory device is designed for use with Intel (Altera) FPGAs and provides non-volatile memory to store configuration bitstreams that are loaded into the FPGA upon power-up or reset. It uses a simple Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) for communication, which ensures a straightforward and efficient connection with FPGAs.
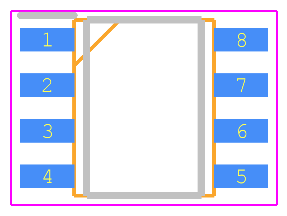
The EPCS4SI8N is available in an 8-pin SOIC (Small Outline Integrated Circuit) package, offering a storage capacity of 4 Mbits (512 KB) of configuration data.
EPCS4SI8N Features
Storage Capacity:
Provides 4 Mbits (512 KB) of storage for FPGA configuration data.
Serial Interface (SPI):
Uses the standard Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) for communication, which simplifies the connection to FPGA devices.
Non-Volatile Memory:
Retains the configuration data even when power is removed, ensuring that the FPGA is automatically configured on power-up.
FPGA Configuration Support:
Supports configuration for Intel (Altera) FPGAs, allowing flexible and efficient bitstream storage.
8-Pin SOIC Package:
Compact 8-pin SOIC package for easy integration into designs with limited board space.
Low Power Consumption:
Optimized for low power consumption, making it suitable for power-sensitive applications.
Reprogrammable:
The device can be reprogrammed multiple times, enabling design updates without changing the hardware.
Temperature Range:
Industrial temperature range from -40°C to +85°C, making it suitable for industrial applications.
EPCS4SI8N Applications
FPGA Configuration:
Primarily used to store configuration data for Intel (Altera) FPGAs, ensuring quick boot-up and reset configurations.
Embedded Systems:
Used in embedded systems that require non-volatile memory for FPGA configuration.
Industrial Automation:
Suitable for industrial control and automation systems where reliable configuration of programmable logic devices is essential.
Consumer Electronics:
Can be used in consumer devices that include FPGAs for flexible logic control, such as set-top boxes, gaming consoles, and smart devices.
Networking Equipment:
Employed in networking equipment where FPGAs are used for packet processing, signal routing, and custom protocols.
EPCS4SI8N Alternatives
If the EPCS4SI8N is not available or does not meet the specific requirements, the following alternatives can be considered:
EPCS1SI8N (Intel/Altera):
A similar product from the same series with a smaller storage capacity of 1 Mbit.
EPCS16SI8N (Intel/Altera):
A higher capacity alternative from the same series with 16 Mbits of storage.
M25P40-VMN6P (Micron):
A 4 Mbit SPI-based Flash memory device that can also be used to store FPGA configuration data.
W25Q32JVSSIQ (Winbond):
A 32 Mbit serial Flash memory device that supports SPI communication and is a suitable replacement for larger storage needs.
AT25DF041B-SH-B (Microchip):
A 4 Mbit serial Flash memory alternative with SPI interface, offering comparable functionality to the EPCS4SI8N.
These alternatives offer varying storage capacities and features, depending on the needs of the specific FPGA-based application.
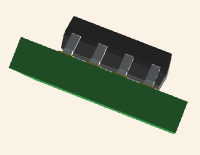
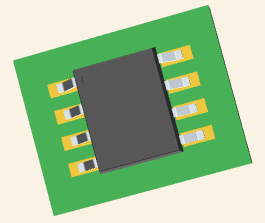
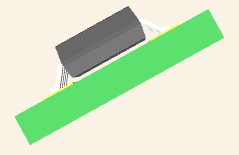
EPCS4SI8N CAD Model
Symbol

Footprint
3D Model
EPCS4SI8N Manufacturer
Altera, founded in 1983, was a leading semiconductor company specializing in programmable logic devices (PLDs), particularly FPGAs (Field-Programmable Gate Arrays), CPLDs (Complex Programmable Logic Devices), and associated tools for hardware and software development. Altera was widely recognized for its innovation in programmable logic solutions, which allowed engineers to design customizable hardware circuits that could be reprogrammed for different applications.
In 2015, Intel Corporation acquired Altera for approximately $16.7 billion, marking a significant expansion into the FPGA market. Following the acquisition, Altera became Intel's Programmable Solutions Group (PSG), continuing the development of its FPGA technology under the Intel umbrella.
Today, Intel (Altera) FPGAs are widely used across various industries, including telecommunications, data centers, automotive, industrial, aerospace, and defense. Intel FPGAs are known for their flexibility, high performance, and the ability to accelerate complex data processing tasks, making them a critical component in many modern technological applications.
EPCS4SI8N FAQ
1. What is the storage capacity of the EPCS4SI8N?
The EPCS4SI8N has a storage capacity of 4 Mbits (512 KB), which is used to store FPGA configuration data for Intel (Altera) FPGAs.
2. Which FPGAs are compatible with the EPCS4SI8N?
The EPCS4SI8N is compatible with Intel (Altera) FPGAs such as the Cyclone, Stratix, and Arria families. It stores configuration bitstreams that are loaded into the FPGA upon power-up or reset.
3. What communication interface does the EPCS4SI8N use?
The EPCS4SI8N uses a Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) for communication, simplifying connectivity with FPGAs and ensuring efficient data transfer.
4. Can the EPCS4SI8N be reprogrammed?
Yes, the EPCS4SI8N is a reprogrammable memory device, allowing you to update the configuration data stored within the device multiple times as needed.
5. What is the package type of the EPCS4SI8N?
The EPCS4SI8N comes in an 8-pin SOIC (Small Outline Integrated Circuit) package, which is compact and suitable for space-constrained designs.




