What are Driverless LED Lights?
2024-12-11 11:02:59 780
The great American businessman and inventor of the light bulb, Thomas Alva Edison, once said, “We shall make electricity so cheap that only the rich will light candles.” That statement has indeed come true today. From small houses to paved roads to big industries, we can notice AC lights illuminating our environment after the sun goes down. Earlier lighting systems used different types of bulbs such as incandescent, Compact Fluorescent Lamps (CFLs) etc. but today with the advancement in LED lighting technology, these incandescent and CFL bulbs are soon being replaced by LED lights. The global LED lighting market continues to grow, reaching $45.57 billion in 2018.
While LED lights are known to be almost 90% more efficient than incandescent bulbs and last longer than other AC bulbs, it still has a drawback. Namely, LED lights are driven by DC voltage, but all of our main power supplies are AC. This prompted designers to use an additional component called an LED driver, which is nothing more than an AC to DC converter. This driver converts AC power from the mains to a suitable DC voltage to power the LED lights. However, AC unmanned LED bulbs were then introduced, which can be plugged directly into the AC power supply without the need for any external driver module. In this article, we will learn more about driverless LED systems and their development over time.
Why driverless LED systems?
The main problem with traditional high power AC/DC switching LED drivers is the power loss associated with them. These traditional AC LED drivers use a switching topology and resistors to control the LED current, and this switching generates heat, which reduces the efficiency of the system. In addition, this extra circuitry leads to an increase in the total cost of the bulb. That's why we discussed low-cost LED driver systems in our last article and even built one to test its performance.
Another terrible problem with AC LED drivers is the flicker effect. As most of us have noticed, older LED driver circuits have a flicker effect. For the most part, these traditional AC LED driver circuits use a half-sine wave at twice the frequency of the power line. This means that in a power line with a frequency of 50 Hz, it produces nearly 100 flashes of light that can be detected by the human eye, which is harmful. This should be eliminated. Therefore, modern techniques using a small number of passive components were introduced to replace the traditional AC-DC converters with switching topologies.
Driverless AC LED lights - work
Driverless LED systems have something called an AC LED light engine. But what is an AC LED light engine? Generally speaking, an engine is used to convert one form of energy into another. For example, an engine is used to convert the heat produced by fuel into the movement of a shaft. Similarly, an AC LED light engine is used to convert electrical energy into lumens of light.
An AC LED light engine is a mechanical device or circuit board in which an LED chip and all electrical connections are mounted. It is an off-the-shelf form of light source that can be easily fixed to an AC socket. It helps LED bulbs as a direct replacement for other conventional lamps.
The development of this AC LED has gone through several stages. It started by simply connecting standard led in series to match the combined forward voltage of the led with the maximum AC input voltage. Lighting those led without any driver sounded like a good idea, but it didn't work. This design has one major drawback, the ac changes its polarity from positive to negative every cycle, so in every positive cycle the led is forward biased (turned on), but in every negative cycle the led is reverse biased, which turns them off.
First generation driverless led
So what was the solution? At this point, the first generation of driverless AC LEDs was introduced, in which each segment of LEDs was replaced with an anti-parallel pair, as shown in the following figure.
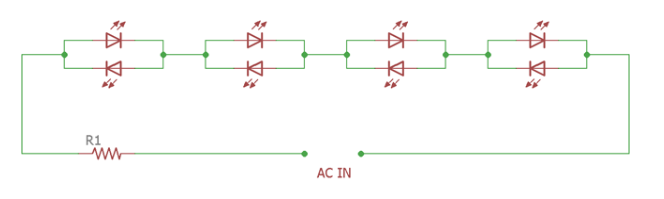
Figure. 1
In the above figure, the led are connected in an anti-parallel fashion. In each positive cycle, one side of the pair is forward biased and the other side is reverse biased, but in the negative cycle, the state changes and the other led lights up. Here the current is limited by a high power resistor R1.
The positive side of the circuit is the efficiency. The efficiency is very high. The in-phase current and voltage waveforms through the circuit produce a high power factor. However, despite the positives mentioned above, the first generation of unmanned LED light engines was a failure. This was due to poorer flicker index and twice the number of led than required. It produces a flashing effect that is easily detected by the human eye and half of the used led remain off for any given time.
Second generation driverless led
To address this shortcoming, a second generation of unmanned AC LED engine was developed. This time the goal was to reduce the LED count. This was only possible by converting AC to DC. Therefore, a bridge rectifier diode was added to the second generation of unmanned AC LED light engines. Except for the rectifier diode, everything in the circuit remains the same.
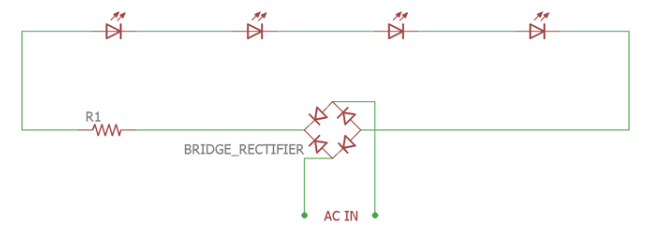
Figure. 2
As before, resistor R1 controls the LED current. Each positive and negative cycle now passes through the led so that they remain on for both cycles.
Third generation driverless led
The introduction of the third generation AC LED engine improves efficiency and yields an enhanced flicker index. Switch controllers have been added to the circuit to individually control the LEDs to a certain level where the power line voltage is the same as the LED voltage. Current limiting functions are also available in the integrated switching controller and can be reconfigured using external components. Such a circuit can provide nearly 80% efficiency and a flicker index of 0.30 to 0.35.
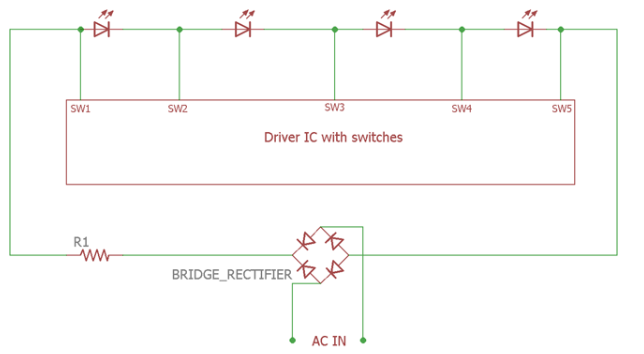
Figure. 3
Fourth generation driverless led
In the fourth generation of unmanned AC LED engines, the controller is eliminated and passive components are used to compensate for manufacturing costs. In addition, the efficiency is superior due to higher power factor and enhanced flicker index.
The circuit operates with two independent current pulses, a capacitive limiting current pulse and a resistive limiting current pulse. These current pulses are fed to the LED string in such a way that the LED string gets two current pulses per half cycle of line voltage. The following figure shows the fourth generation low power unmanned AC LED light engine circuit.

Figure. 4
The principle of operation of the above circuit is very interesting. During the first half cycle of the input AC, the current passes through resistor R1, eventually charging capacitor C1, and returns to the bridge rectifier diode through the second string of led, charging capacitor C2 and resistor R2. During negative peaks, capacitor C4 discharges C1 and C2 accordingly and pushes current through the second string. As a result, the current required to light the LED string does not flow completely through the resistors during each cycle. Almost 40-50% of the total current passes through the resistors, increasing the efficiency to 90% by reducing heat dissipation.
The input waveform of the led and the input AC voltage can be seen in the following figure.
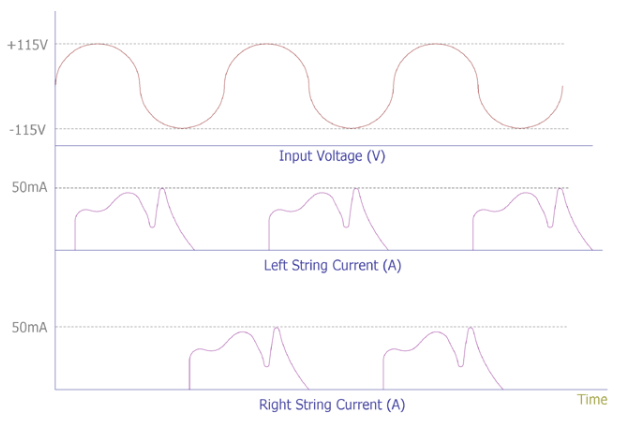
Figure. 5
The above figure shows three plots: input voltage, left LED string current and right LED string current over time. At 230V line voltage, the LED strings light up alternately. This is a very fast transition in the millisecond range.
Advantages of driverless LED light technology
These driverless LED lights are easier to manufacture. Reduced cost and require very little maintenance.
due to improved flicker index it can be used for high bay lights. Also, offices, rooms, education sector are using driverless AC LED lights.
after removing the LED driver, it enables the reshaping feature. the LED products can be made in different shapes and sizes.
Easy and quick installation is another great feature of driverless AC LED lights.
Driverless LED Lights Manufacturer
Driverless AC LED lights are selling like hot cakes today. Different manufacturers are producing different types of driverless AC LED technology. China is one of the major suppliers of driverless AC LED lights. However, several companies are also producing led with high forward voltage and high lumens. high forward voltage LEDs provide low component counts in driverless ac LED systems. Some of the popular manufacturers of driverless AC LEDs in this segment are Cree, LUMILEDS, SAMSUNG, NMB Technologies, Opulent etc.




