What is a Microcontroller Unit (MCU)? Uses, Features, and Applications Explained
2025-04-27 11:54:03 832
What is Microcontroller Unit?
The microcontroller unit, sometimes referred to as the central processor unit (CPU), is a single chip that combines LCD driver circuitry, memory, counters, USB, A/D conversion, UART, PLC, DMA, and other peripheral interfaces. As a result, a chip-level computer is produced that can execute different control combinations for different applications. There are numerous ways to control different applications with the chip. The figure of the Microcontroller Unit may show devices like cell phones, PC peripherals, remote controls, automotive electronics, industrial stepper motors, robot arm control, etc.
In order to meet the demands of product development in the green era, many microcontroller unit operators are also continuing to create energy-saving designs for 8-bit microcontroller unit frequency adjustment. These units, which run at frequencies between 16 and 50 MHz and stress simple performance and low-cost applications, continue to occupy a certain position in the present microcontroller unit market value.
Due to the emergence of 32-bit microcontroller units and ongoing price reductions, as well as the simple, long-lasting, and low-cost advantage of 8-bit microcontroller units, the market for 16-bit microcontroller units continues to be squeezed, becoming the lowest proportion of product shipments. The mainstream specifications for 16-bit microcontroller units include 16-bit operation, 16/24-bit addressing capability, and frequency of 24~100MHz. Additionally, some 16-bit microcontroller units provide additional 32-bit addition/subtraction/multiplication/division special instructions.
32-bit Microcontroller Unit can be said to be the mainstream of the Microcontroller Unit market, with a single price between $1.5 and $4, an operating frequency mostly between 100 and 350MHz, better execution performance, and a wide range of application types. However, 32-bit Microcontroller Units will be due to the increase in the number of operations and the length of the memory, the length of the program code for the same function increases by 30~40% compared to 8/16bit Microcontroller Units, which leads to the embedded OTP/FlashROM memory capacity can not be too small, and the chip external footage number skyrocketed, further limiting the ability to reduce the cost of 32bit Microcontroller Units.
Microcontroller Unit have the following characteristics:
High degree of integration: Microcontroller Unit chips integrate the processor, memory, peripheral interfaces, and other functional modules internally, allowing the entire system to be completed on a single chip; Low power consumption: These chips are typically made to use less power in order to save energy or prolong battery life; Strong real-time performance: These chips must respond to external events and signals in real-time, with high real-time performance and response speed; Easy to use: These chips offer a plethora of development tools and environments, making it simple for developers to program and create applications; Cost-effective: Because of their high degree of integration and functional specialization, Microcontroller Unit chips are reasonably priced and appropriate for large-scale applications and projects with a tight budget.
Composition of Microcontroller Unit
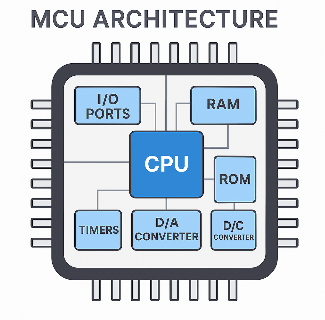
MCU Architecture
Microcontroller Unit is mainly composed of a central processor CPU, memory (ROM and RAM), input/output I/O interfaces, serial ports, counters and so on.
CPU: The central processing unit is the central component of the microcontroller unit. The operation component can perform bit variable processing, arithmetic logic operations on data, and data transmission operations, while the control component analyzes and carries out instructions and coordinates the work in accordance with a predetermined time sequence.
ROM: Read-Only Memory is the program memory, which is used to store the program written by the manufacturer, and the information is read in a non-destructive way, and the saved data will not disappear when the power is turned off, and the Microcontroller Unit will process it according to the pre-programmed program.
RAM: Random Access Memory, is the data memory, and the CPU direct data exchange, after power down this data can not be maintained. It can be written and read at any time when the program is running, and is generally used as a temporary data storage medium for the operating system or other running programs.
Classification of Microcontroller Unit
There are two types of microcontroller units: general-purpose and specialized. The former refers to the development of resources (ROM, RAM, I/O, EPROM, etc.) and all other resources that are provided to the user's microcontroller unit; the latter refers to the hardware and instructions that are designed in accordance with a specific purpose, such as a motor controller, printer controller, tape recorder movement controller, etc. The latter is classified into 1-bit, 4-bit, 8-bit, 16-bit, 32-bit, and even 64-bit microcontroller units based on the width of the bus or data register.
By memory type - Microcontroller Units can be categorized into two types: without on-chip ROM type and with on-chip ROM type.
According to the memory structure - Microcontroller Unit according to its memory structure can be divided into Harvard (Harvard) structure and von ▪ Neumann (Von Neumann) structure.
According to the instruction structure - according to the instruction structure can be divided into CISC (Complex Instruction Set Computer, Complex Instruction Set Computer) and RISC (Reduced Instruction Set Comuter, Streamlined Instruction Set Computer). microcontroller)
What is the use of Microcontroller Unit
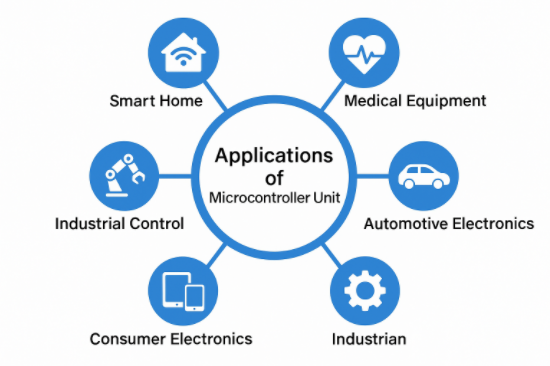
MCU Applications
In many embedded control systems, a microcontroller unit (Microcontroller Unit) is a chip that combines a CPU core, memory, and input/output interfaces. The following categories can be used to classify its uses:
Control function: A microcontroller unit can be used to regulate the state of operation of a variety of physical components, including electric motors, LED lights, and motors. In order to control the fan speed, light brightness, or appliance operation mode, for example, it can process external input signals and determine the appropriate actions for the devices.
Communication function: To exchange data with other devices or systems, the microcontroller unit supports a number of communication interfaces, including I2C, SPI, UART, CAN, USB, and others. In IoT devices, Microcontroller Units are commonly used to communicate with wireless
Microcontroller Units are frequently used in Internet of Things devices to interface with wireless modules like Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, ZigBee, etc.
Signal Processing: Microcontroller Units are used extensively in industrial instruments, health equipment, environmental monitoring, and other fields. They can gather analog signals from sensors, convert them to digital signals for processing using the integrated ADC (analog-to-digital converter), or output analog signals using DAC (digital-to-analog converter).
Automation control: Microcontroller Units can make logical decisions to enable automatic equipment functioning in automation settings. Microcontroller units, for instance, can regulate the time and action of each program stage in a washing machine and enable real-time monitoring and control in an industrial production line.
Security and encryption: Some Microcontroller Units are equipped with security modules for encryption computing, identity authentication, anti-tampering and other functions, which are commonly used in payment devices, security locks, access control systems and other scenarios that have requirements for data security.
Energy-saving management: Microcontroller Units can dynamically adjust their operating state according to the system load, enter low-power or hibernation mode to extend battery life, and are widely used in portable devices, wearable devices and wireless sensing nodes.
Common application areas include smart home, medical equipment, industrial control, automotive electronics, consumer electronics and so on. Due to its low price, flexible functions and low power consumption, Microcontroller Unit has become an indispensable core component in many electronic products.




